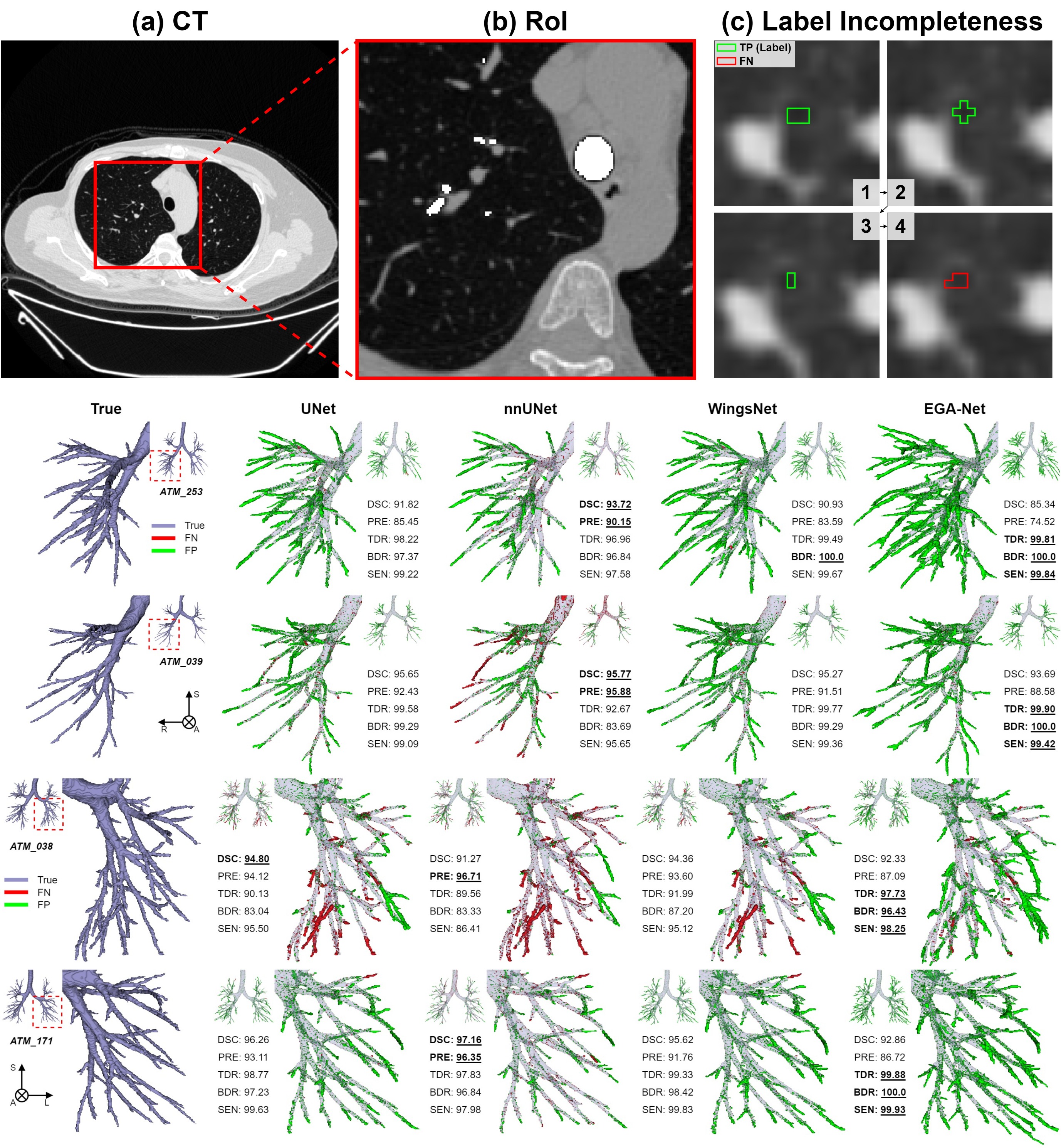
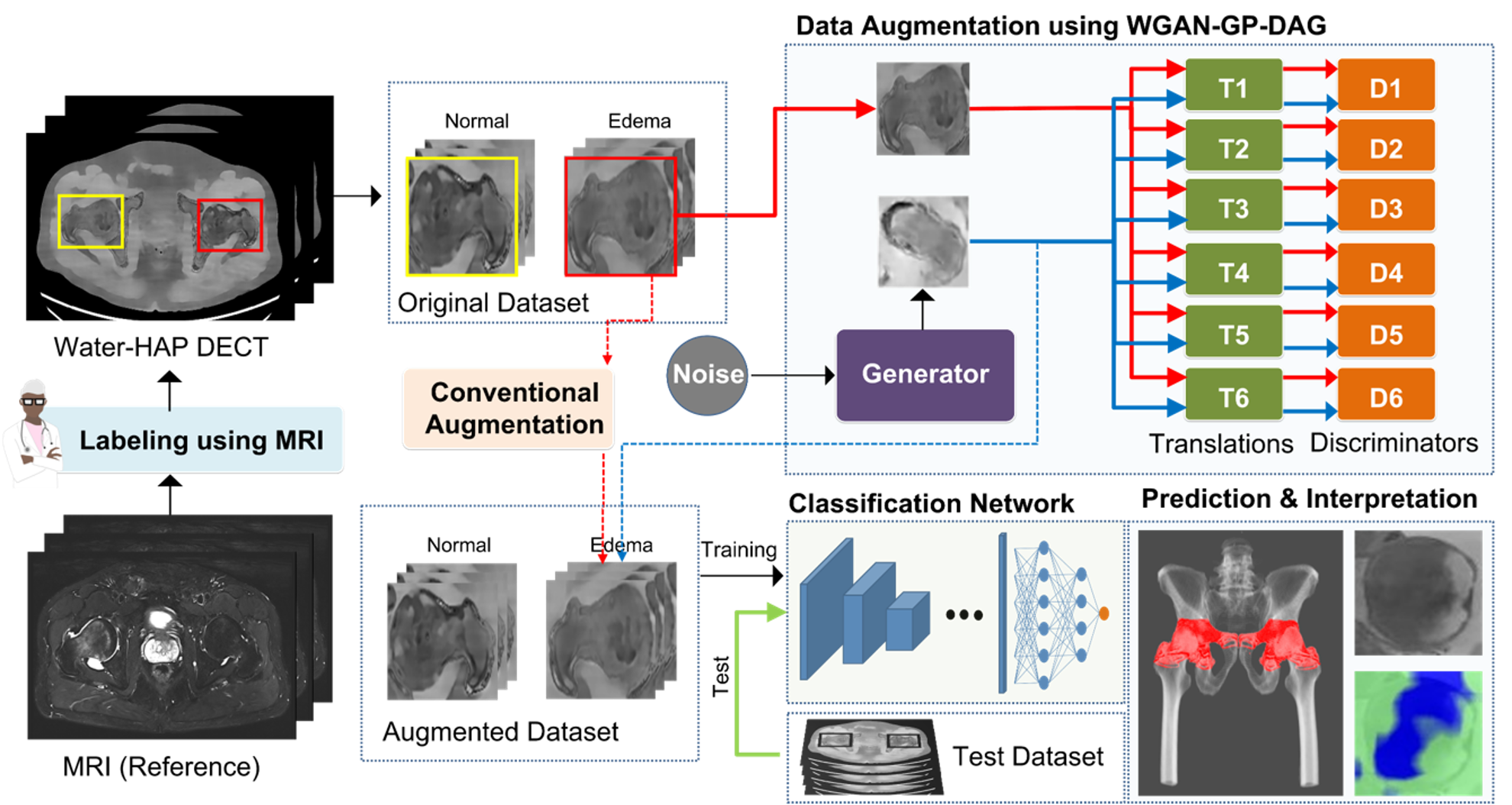
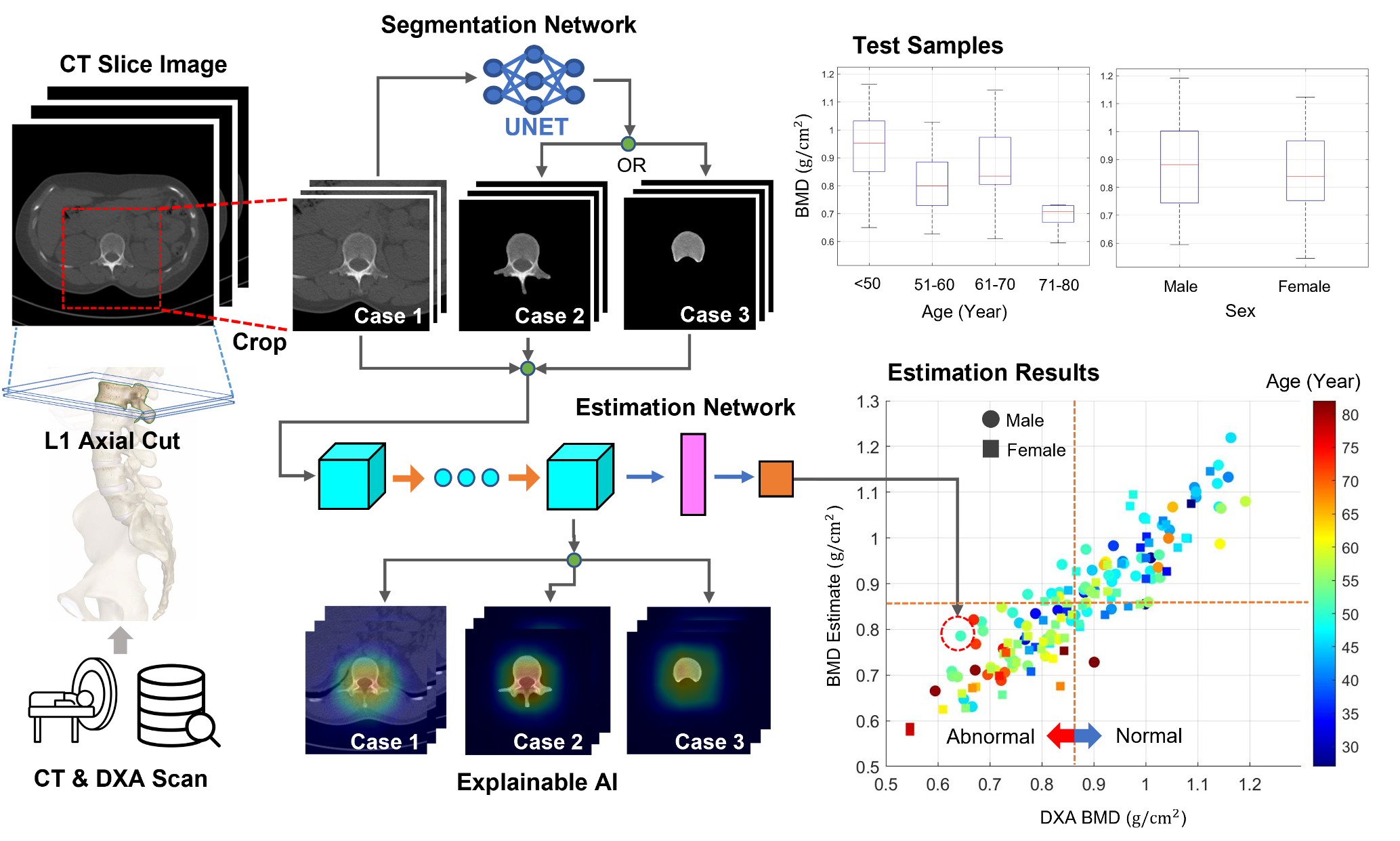
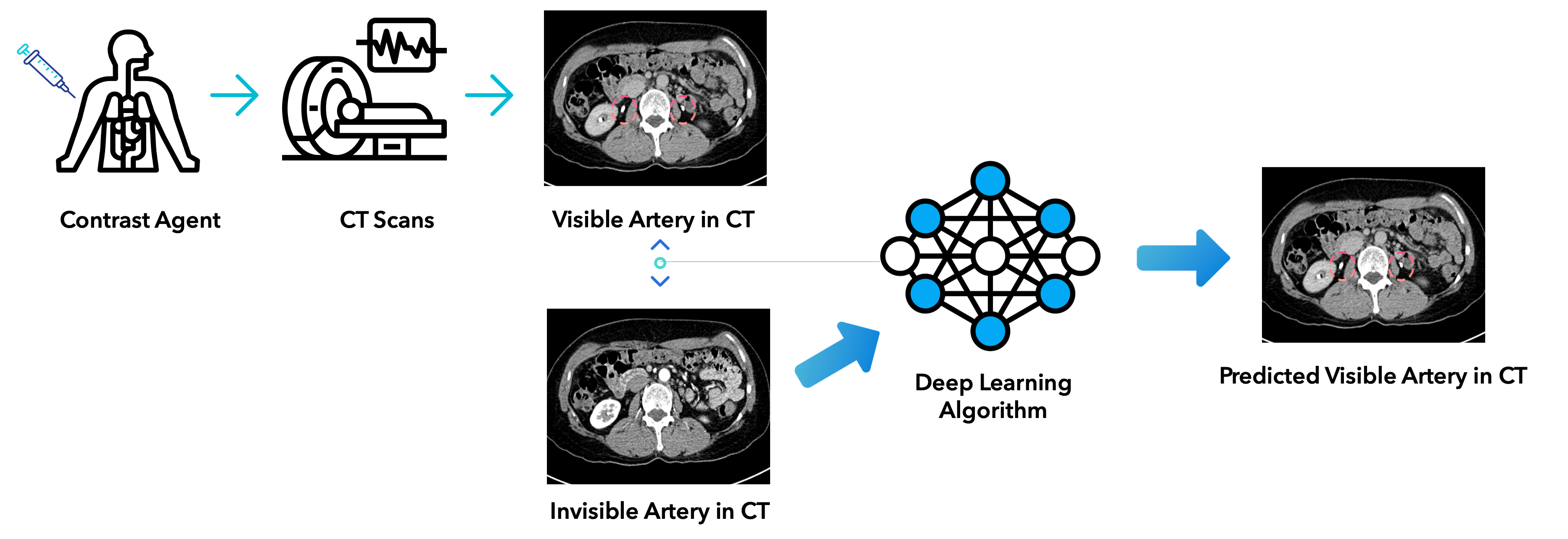
While invasive procedures such as thoracoscopy can be used for tissue biopsy in the chest, they often increase the patient’s burden and may result in poor clinical outcomes. As a less invasive alternative, tissue samples can be collected through bronchoscopy. However, this requires a detailed map of the airway to navigate toward the target lesion. Conventional pixel intensity-based airway segmentation methods suffer from high false-positive rates (FPR) and often fail to detect small peripheral airways. To overcome these limitations, deep learning (DL)-based approaches have been proposed, resulting in improved scores. Nevertheless, they still exhibit limited sensitivity for fine airways, and the incompleteness of ground-truth labels for supervised learning poses additional challenges. In this study, we propose an Encoder-Guided Attention U-Net to enhance the sensitivity of airway detection in chest CT images. The proposed model is capable of detecting deeper and finer airway branches even under incomplete supervision. It achieved state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in terms of Tree Detection Ratio (TDR) and Branch Detection Ratio (BDR) in the long-term validation phase of the ATM’22 Challenge. In this study, we are collaborating with the Department of Respiratory Medicine at Yangsan Pusan National University Hospital to develop a new image-guided method based on deep learning that can provide easy and accurate guidance for accessing peripheral lesions, aiming to overcome the limitations of peripheral lung lesion tissue biopsy and successfully perform early lung cancer tissue examination.